Quartz crucibles are a specialized product within quartz glass products. They are containers used in the photovoltaic and semiconductor industries to hold molten silicon and form silicon ingots. Due to the properties of quartz crucibles such as cleanliness, homogeneity and high-temperature resistance. In terms of physical and thermal properties, its deformation point is approximately 1100℃, its softening point is 1730℃, and its maximum continuous service temperature is 1100℃, with a short-term maximum of 1450℃. It is currently widely used in the production process of extracting crystalline silicon in the solar energy and semiconductor fields and is a consumable in the production process of crystalline silicon.
The production of semiconductor quartz crucibles and photovoltaic quartz crucibles both follow the same process flow: Firstly, through the use of centrifugal force and forming devices, quartz sand raw materials are formed into a certain shape and thickness in a rotating quartz crucible mold. With high-temperature electric arcs as the heat source, the quartz sand raw materials in the quartz crucible mold are melted at high temperatures. After the melting is completed, the quartz crucible blanks are taken out. Place the quartz crucible with the end facing down on the working platform. Use grinding equipment or various sandblasting devices to remove the sand adhering to the outer surface of the quartz crucible. Then, use the edge trimming and chamfering equipment and centering device to correct the quartz crucible. According to the height requirements, use the cutting device to cut the quartz crucible. Finally, use the inner and outer chamfering devices to chamfer the cut end face of the quartz crucible as required.
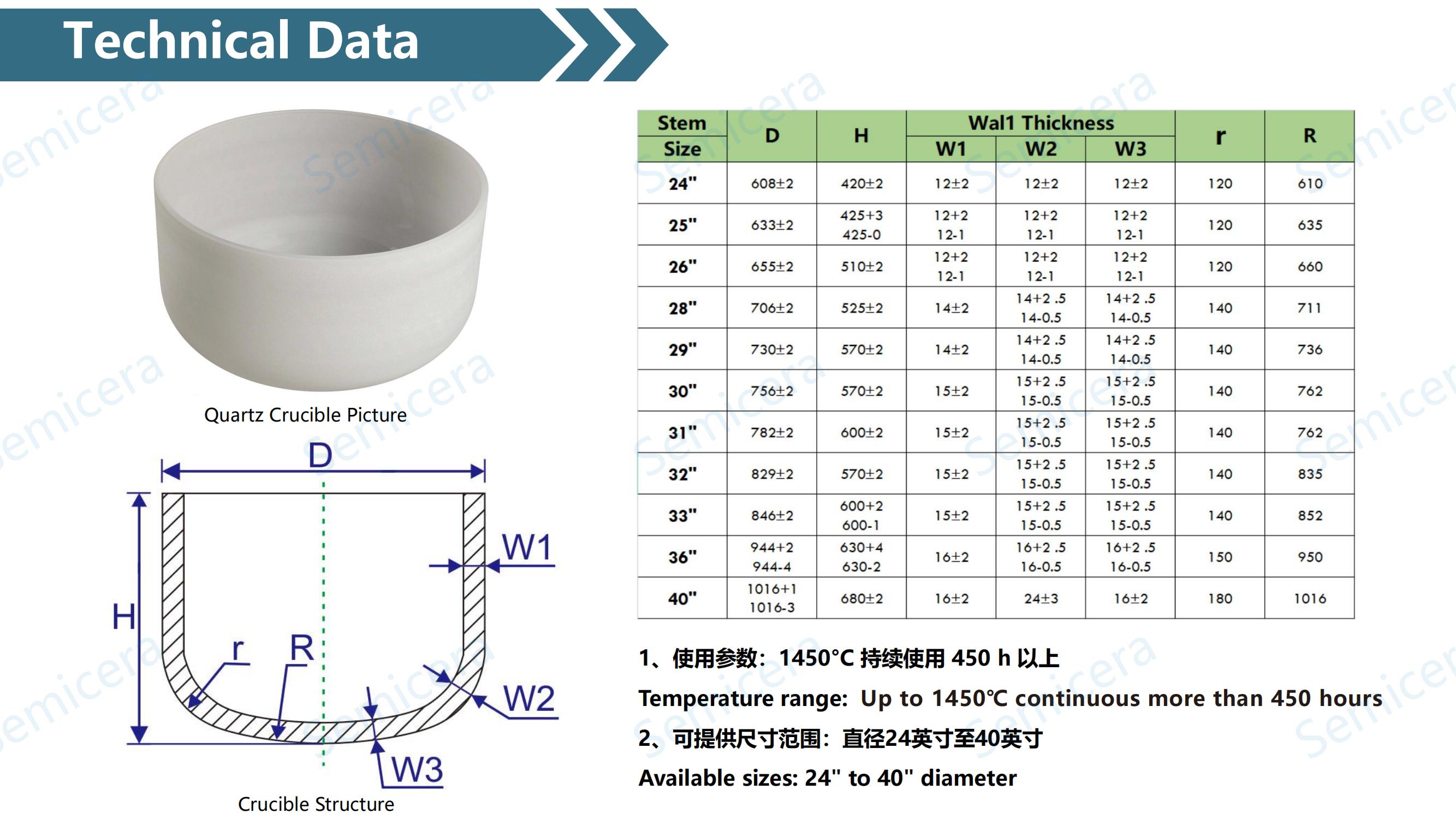
The quartz crucible presents a double-layer structure both inside and out. Early quartz crucibles had a fully transparent structure. This transparent structure was prone to causing uneven heat transfer conditions, increasing the difficulty of crystal rod growth. Moreover, the uniform structure required a large amount of high-quality, high-purity quartz sand and was costly. Therefore, the preparation method of this type of quartz crucible was basically phased out. Quartz crucibles prepared by the arc method are semi-transparent and have an inner and outer layer structure. The outer layer is a region with high bubble density, known as the bubble composite layer. The bubble composite layer is heated more evenly and has a better heat preservation effect. The inner layer is a transparent layer of 3-5mm, known as the bubble depletion layer. The presence of the bubble depletion layer reduces the bubble density in the contact area between the crucible and the solution, thereby improving the success rate of single crystal growth and the quality of the crystal rods.
The purity of quartz sand significantly affects the quality of crystal pulling. During the crystal pulling process, the content of hydroxyl groups, impurity elements and bubbles inside the quartz crucible will affect the quality of the silicon rod and the service life of the quartz crucible. Among them, the process route can improve the content of hydroxyl groups, but the content of impurities and bubbles more depends on the purity of the quartz sand itself.